Dezincification is the corrosion brass alloys where the Zn in the alloy reacts preferentially in a corrosive environment. Basically zinc is lost and porous copper is left behind. Red brass (i.e. <15 wt% Zn) does exhibit dezincification; however, the occurrence is rare because the Zn is absorbed in the copper matrix. Yellow brass with >25wt% Zn is more susceptible to dezincification. This is because there are separate zinc rich regions in the alloy that are sacrificed to the more noble copper rich regions. Ultimately he high zinc regions are removed from the alloy by a microscopic galvanic corrosion (See Figure #1). Simple fittings can be made with red brass. However, for complicated valves, such as flow control valves or isolator valves, which require forging and complex machining, leaded yellow brass chosen. Because lead presents health issues, new low lead yellow brass alloys have been recently developed.

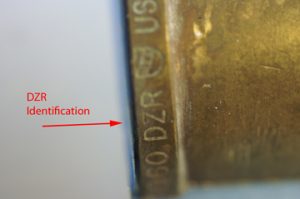
As a response to dezincification, brass companies have developed dezincification resistant alloys, and the components are stamped” DZR”. Unfortunately, under certain conditions these alloys can exhibit dezincification.